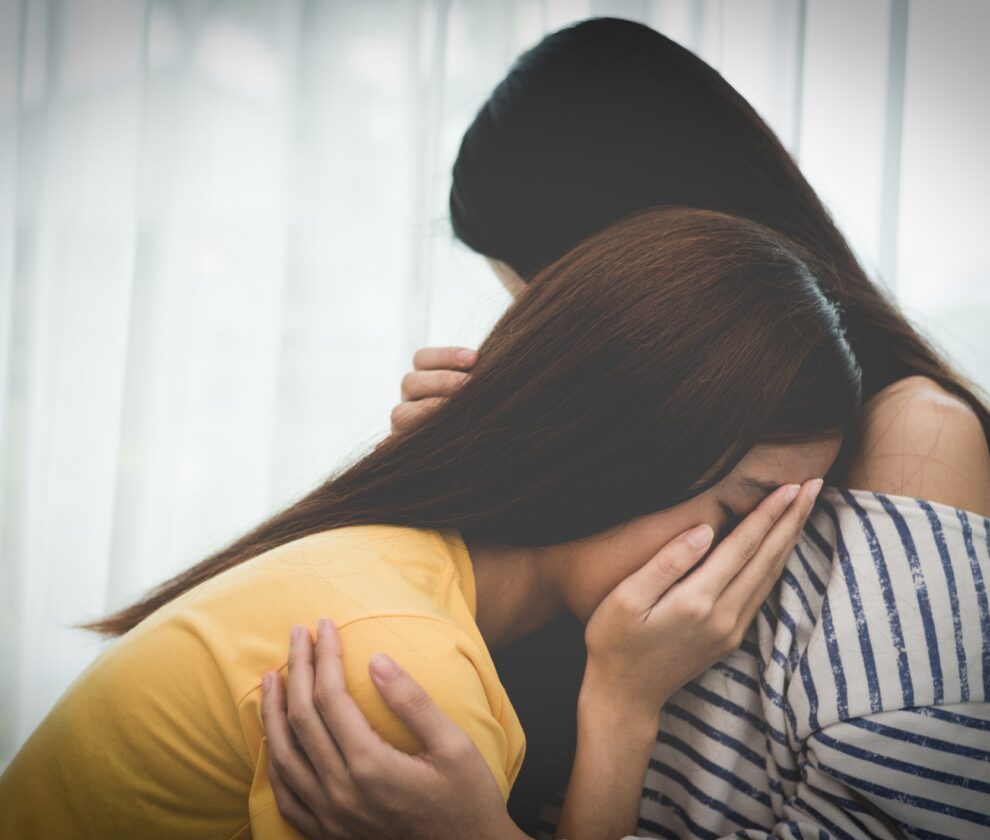
Have you ever felt really down after spending time with someone who’s sad all the time? Maybe you noticed your energy drop, or you started feeling heavy inside without knowing why. That’s what makes people ask, “Is depression contagious?”
The answer is a little tricky. You can’t catch depression like the flu, but emotions can spread from one person to another. A study published in The Lancet revealed a 25% increase in depression worldwide in 2020, showing just how much stress and change can affect people’s mental health.
When someone close to you is struggling, their sadness can rub off on you. That’s called emotional contagion, and it’s something your brain naturally does. This can happen even if you’re dealing with high-functioning depression yourself or supporting someone with complex grief.
What depression is, how it can feel like it spreads, and what to do if you think you’re carrying someone else’s emotional weight. You’ll also learn how to care for others without losing yourself in the process. If you’ve ever wondered whether depression can make you sick or how mental health affects your body, this guide will help you understand and protect your emotional balance.
What Is Depression?
Depression is more than just feeling sad. Everyone feels down sometimes, but depression is when that sadness sticks around for a long time, weeks or even months. It can make people feel tired all the time, lose interest in things they once loved, or feel hopeless for no clear reason.
It’s not just “in your head.” Depression is a real health condition that affects the way someone thinks, feels, and acts. It can make everyday things like eating, sleeping, or even getting out of bed really hard.
The good news is that depression is treatable, and no one has to deal with it alone. Some common signs of depression:
- Feeling sad or empty most of the time
- Sleeping too much or too little
- Losing interest in fun things
- Feeling tired or having no energy
- Thinking “I’m not good enough”
- Wanting to be alone all the time
If someone around you shows these signs often, they might be dealing with depression, and it’s okay to ask for help through therapy.
How Depression Is Contagious
Now that we know what depression is, here’s something surprising: It can feel contagious, even though it’s not like a cold or flu. This happens through something called emotional contagion, when we start feeling the emotions of people around us.
Our brains are wired with special cells called mirror neurons. These help us feel what other people feel, which is great for understanding others, but it also means we can soak up their sadness without realizing it.
If someone you care about is always feeling down, you might start to feel heavy or low, too. This is your brain trying to connect and show empathy, but if you’re not careful, it can leave you feeling just as tired as the person you’re trying to help.
| Catching a Cold | Feeling Someone’s Depression |
|---|---|
| Caused by germs | Caused by shared emotions and energy |
| Spreads through touch or air | Spreads through time and closeness |
| Happens quickly | Happens slowly over days or weeks |
| Needs medicine | Needs support, rest, and sometimes therapy |
So no, depression isn’t contagious like a sickness, but the feelings can be shared if we don’t protect our mental space.
So How Exactly Is Depression Spread?
You don’t catch depression from someone like you catch a virus, but you can take on someone else’s sadness by being around them a lot, especially if you care about them deeply. This happens slowly, through things like body language, tone of voice, and the energy in a room.
Common Ways Depression Spreads Emotionally:
- Close relationships: If your friend, parent, or sibling is always sad, you might feel it too. This is common in people living with a spouse with mental illness or supporting a grown child with depression.
- Negative environments: Homes, schools, or teams with low energy or lots of stress can pull your mood down.
- Social media: Watching sad or angry posts, venting videos, or bad news all day can change how you feel.
- Trying too hard to help: If you’re always “saving” someone, your own heart can start feeling heavy. In some cases, this may even resemble high-functioning depression.
Who’s More Susceptible to ‘Catching’ Depression?
Some people feel emotions more strongly than others. If you’re someone who really cares about people, notices small changes in mood, or feels sad when your friend is sad, you might be more likely to “catch” someone else’s emotional pain.
This doesn’t mean something is wrong with you. It just means your heart is very open, and sometimes it opens too wide. These people are often called empaths or highly sensitive people (HSPs). They are great listeners, kind friends, and caring helpers, but they also get tired more easily from other people’s emotions. You might be more affected if you:
- Worrying a lot about how others feel
- Try to fix everyone’s problems
- Feeling tired after hanging out with someone sad
- Notice every little shift in someone’s mood
- Cry easily, even during movies or stories
If this sounds like you, that’s okay! It just means you need to protect your energy while still being kind. You may also want to learn about high-functioning depression, which often hides under constant emotional caregiving.
Fun Metaphor: Sponge vs. Umbrella
- A sponge soaks up everything around it, even when it’s full
- An umbrella notices the rain but stays dry underneath
If you’re more like a sponge, you may need to learn how to let go of emotions that don’t belong to you. Supportive therapy like CBT or EMDR for anxiety can help build those emotional boundaries.
Who Can I Get It From?
You can start feeling someone else’s depression from anyone you’re emotionally connected to. It doesn’t matter how old they are, where they live, or if you see them in person or online.
The stronger the bond, the easier it is to pick up on their mood. Even if they don’t say much, your heart might notice something’s wrong, and that’s when emotional contagion can begin.
Common Sources of Emotional Contagion:
- A parent or spouse with mental illness
- A sibling who’s withdrawn or irritable
- A friend who talks a lot about hopelessness
- A teacher or coach who’s under pressure
- Online creators discussing depression
You can love these people and still need a break. Caring isn’t the same as carrying, and you don’t have to hold everyone’s feelings to prove you care.
What Will I Experience?
When you’re around someone who’s struggling with depression, you might start to feel different without knowing why. Maybe you used to laugh a lot, but now you feel quiet and tired. Maybe your thoughts feel cloudy, or things that used to be fun just feel “meh.”
This doesn’t mean you’re depressed, but it might mean your emotions are picking up too much from someone else. Your brain is trying to help, but it might be doing too much.
Signs You Might Be Absorbing Someone Else’s Emotions:
- Feeling tired for no reason
- Getting sad, cranky, or moody suddenly
- Losing interest in fun activities
- Trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
- Feeling like you’re carrying a heavy invisible weight
- Getting emotional over small things
These are signs your body and brain are asking for a reset. And that’s totally okay, you can recharge, set boundaries, and feel like you again. Consider checking out our guide to why depression makes you tired or therapy for depression in Georgia to support your emotional health.
What Do I Do If I’ve ‘Caught’ Depression?
If you’ve been feeling heavy, tired, or sad after being around someone who’s struggling, that doesn’t mean something is wrong with you. It means your heart has been doing a lot of emotional work and now it’s your turn to rest, recharge, and get support.
You can still be a good friend, partner, or family member while taking care of yourself. In fact, when you feel stronger inside, you’re even better at helping others. Sometimes, just hearing “me too” from someone else can make a huge difference. Support groups, either in person or online bring together people going through similar things. You can talk, listen, or just sit quietly and feel understood.
See a Therapist Together
If you and someone close to you are both feeling low, try seeing a licensed therapist in Georgia together. This could be a family member, a partner, or a close friend. Family therapy helps you talk through feelings in a safe, peaceful space where no one gets blamed. It can build stronger trust and better communication.
Support Each Other
Sometimes, the best thing you can say is, “I’m here for you.” You don’t have to give advice or solve anything. Just sitting with someone, checking in with them, or asking, “Do you want to talk or just hang out?” shows that you care. And don’t forget to ask for support, too, you matter just as much. If you’re struggling to hold it together while appearing fine on the outside, you might want to learn more about high-functioning anxiety and how it affects caregivers.
Meditate Together
Meditation isn’t about being perfect. It’s just a quiet moment to breathe and calm your mind. Try doing a 5-minute meditation with a friend or loved one. Apps like Calm, Headspace, or even free YouTube videos can guide you through breathing, relaxation, or gentle body awareness. Or, explore mindfulness-based options through EMDR therapy for anxiety if emotional overload is building up.
Seek Help
If your sadness keeps growing, or if things just feel too big to handle alone, it’s time to reach out. Talk to a school counselor, a trusted adult, or a mental health professional. Getting help doesn’t make you weak, it shows you’re strong enough to care for yourself.
Need someone to talk to? At Novu Wellness, caring professionals are ready to help you feel like yourself again.
What If I’m Feeling This Due to My Social Media Habits?
Sometimes, the sadness we carry doesn’t come from people around us but from what we scroll. Social media is full of stories, venting, and highlight reels. While some posts are helpful, too much can quietly wear you down. You may notice your mood drop, feel worried, or start comparing yourself to others without meaning to.
Signs Social Media Might Be Affecting Your Mood:
- You feel sad, worried, or “off” after scrolling
- You compare yourself to others constantly
- You feel guilty for not doing enough in life
- You see lots of sad, venting, or hopeless content
- You can’t stop scrolling, even when you want to
What You Can Do:
- Take a break from social apps, even just for one day
- Unfollow or mute pages that bring you down
- Follow accounts that post kind, funny, or uplifting things
- Talk to someone in real life when your brain feels overloaded
- Remember: people post the best (and worst) parts, not the full story
What If I’m the One “Spreading” Depression?
This is a big and brave question, and if you’re asking it, it already shows how much you care about others. If you’ve been going through something hard and you’re worried that your sadness is affecting the people around you, just know this: You are not a burden.
Everyone has hard days. Everyone feels low sometimes. Sharing your feelings doesn’t make you a problem it means you’re human. Still, it’s okay to learn how to share in ways that feel healthy for both you and the people you care about.
Healthy Ways to Express Tough Emotions:
- Say things like: “I’m having a hard day, but I don’t expect you to fix it.”
- Ask before venting: “Can I talk about something heavy right now?”
- Journal your feelings or record a voice note just for you
- Talk to a therapist who can hold that emotional space
- Check in with others, too: “How are you doing?”
Talking about your pain is not wrong. Just make sure you’re not carrying it alone or placing it fully in someone else’s lap. You deserve help just like anyone else. If the emotions are tied to something deeper like bipolar disorder, or if you’re unsure, professional support can help you get clarity.
Can Depression Spread Within Families or Households?
Yes, it really can feel like depression spreads inside a family or home. When one person in a house is struggling, their mood can affect everyone else, even if they don’t mean to. Homes are shared spaces, and so are emotions. If a parent, sibling, or partner is going through a dark time, the overall mood of the house can start to feel heavy, quiet, or tense.
Children and teens especially soak up the emotions around them. They might not always understand what’s happening, but their brains and bodies still feel it. This emotional ripple can show up as tiredness, stress, acting out, or shutting down. If your child is showing signs, it may be time to explore mental health support for teens in Georgia.
The good news? There are small, powerful things families can do to keep emotional balance even when someone is dealing with depression.
Tips for Protecting Emotional Health at Home:
- Talk openly and gently about feelings (no pressure)
- Keep simple routines like dinner together or quiet time
- Make space for laughter and joy, it’s okay to feel happy, too
- Let each person have their own space when needed
- Consider family therapy to grow stronger together
Depression doesn’t make someone a bad parent, sibling, or child. But emotional health in homes works best when everyone shares the care, not just the struggle.
What’s the Difference Between Helping and Absorbing?
Sometimes, the line between being helpful and taking on too much gets blurry, especially if you’re the kind of person who wants to fix everything. But supporting someone doesn’t mean you have to feel what they’re feeling or carry their pain like it’s your own. Let’s break it down:
| Helping | Absorbing |
|---|---|
| Listening with care | Feeling drained after every conversation |
| Offering support, not solutions | Trying to fix everything yourself |
| Encouraging them to get help | Believing it’s your job to make them better |
| Setting healthy limits | Saying yes even when you’re overwhelmed |
| Caring without losing your peace | Feeling responsible for their every emotion |
Ask Yourself:
- Am I still taking care of myself?
- Do I feel guilty when I take a break?
- Do I feel responsible for this person’s happiness?
If the answer is “yes” too often, you may be absorbing instead of supporting. You can care deeply without giving up your emotional safety. Setting boundaries is one of the most powerful ways to truly help someone.
Need help figuring out those boundaries? Talk to a therapist who understands high-functioning anxiety and the emotional load many caregivers carry.
Is There a Biological Basis for Emotional Contagion?
Yes! Emotional contagion isn’t just “in your head”; it’s built into how your brain works. Scientists have discovered that our brains are wired to feel what others feel, thanks to something called mirror neurons.
These special brain cells fire when we see someone else experiencing an emotion, like sadness or joy. It’s your brain’s way of saying, “Hey, pay attention! That person’s feeling something important.” This helps us connect, understand, and respond with care but it can also cause us to take on emotions that don’t belong to us.
Brain Areas Involved in Emotional Contagion:
| Brain Region | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Mirror Neurons | Let you feel what others feel (empathy in action) |
| Amygdala | Triggers emotions like fear or sadness |
| Anterior Insula | Helps you understand and feel other people’s pain |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Helps you respond calmly and make thoughtful choices |
So yes, if you feel like you’re “catching” someone’s emotions, it’s because your brain is designed to connect, but just like muscles, your emotional brain needs rest too. If it’s impacting your daily life, consider therapy for anxiety or mood issues to reset your mental wellness.
How to Talk to Someone If Their Sadness Is Affecting You
This might feel scar,y but having this kind of honest conversation can save your emotional energy and protect the relationship. You don’t need to blame or make them feel worse. Just speak from your heart, kindly and clearly.
Tips for Starting the Conversation:
- Use “I” statements
Say: “I’ve been feeling heavy lately, and I think it might be from carrying too much emotion.”
Don’t say: “You’re making me depressed.” - Choose a calm time, not during a fight or crisis
- Be gentle and open to how they respond
- Make it clear you still care, you’re just trying to protect your peace, too
Sample Script:
“I care about you so much, and I want to be there for you. But I’ve also been feeling really low myself. I think I need a little space or help, so I can keep showing up for you without burning out.”
If it feels too hard to say out loud, consider exploring this in individual counseling or relationship therapy.
Conclusion
Let’s be honest: being around someone who’s depressed can feel heavy. But it doesn’t mean you’re weak. It means you’re human. Emotions are powerful, and when you care deeply, you might start feeling them in your own heart.
But here’s the truth: you can care without carrying everything. You can love someone and still need rest. You can support them and still say, “I need a break.” That’s not selfish, it’s smart and strong.
Gentle Reminders:
- You are not responsible for anyone else’s healing
- You are allowed to set emotional boundaries
- You can feel joy even if someone you love is sad
- You deserve care, too
- Help is available, and asking for it is brave
If you or someone you care about is struggling, don’t wait. Talk to someone or reach out to a licensed professional.
Novu Wellness offers compassionate, expert care to help you and your loved ones feel better together.